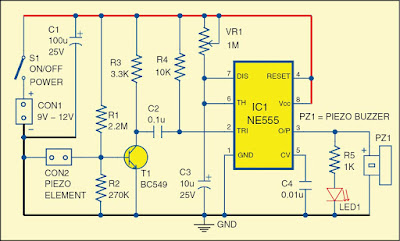
This circuit can be used for sounding an alarm to detect the breaking of a glass window by an intruder, even when the intruder ensures there is no sound of the shattered glass.
Fig. 1: Circuit of the glass break alarm
Circuit and working
Fig. 1 shows the circuit diagram of the glass break alarm. It is built around a piezo element connected across connector CON2, transistor BC549 (T1), timer NE555 (IC1), a piezo buzzer (PZ1) and a few other components.
 A small piezo element used in the piezo buzzer is used as a sensor. It may be fixed at the centre of the window glass. IC1 is wired in monostable multivibrator mode, which is triggered by the piezo element. Output of IC1 is used to drive piezo buzzer PZ1. LED1 indicates the high-state output at pin 3 of IC1. Time delay can be adjusted by potentiometer VR1. Use an ordinary piezo buzzer at the output to generate a warning sound. This circuit works on 9V-12V DC.
A small piezo element used in the piezo buzzer is used as a sensor. It may be fixed at the centre of the window glass. IC1 is wired in monostable multivibrator mode, which is triggered by the piezo element. Output of IC1 is used to drive piezo buzzer PZ1. LED1 indicates the high-state output at pin 3 of IC1. Time delay can be adjusted by potentiometer VR1. Use an ordinary piezo buzzer at the output to generate a warning sound. This circuit works on 9V-12V DC.
When an intruder tries to break the glass, the piezo element generates an electric pulse, which is amplified and sent to the monostable multi-vibrator (IC1). The high output of IC1 drives LED1 and also produces a sound to indicate that someone is breaking the glass.
The 9V-12V DC power supply is connected across CON1, and the piezo element is connected across connector CON2.
Construction and testing
An actual-size, single-side PCB for the glass break alarm is shown in Fig. 2 and its component layout in Fig. 3. Enclose the PCB in a suitable small box in such a way that the piezo buzzer sounds when someone tries to break the glass window. Fix the piezo element at the centre of the window glass for best results.
Fig. 3: Component layout of the PCB
Use of 8-pin IC base is recommended for IC NE555.